Virtual Servers vs Physical Servers: Which is Right for Your Organization?
Introduction:
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, organizations must make crucial decisions about their infrastructure. One of the most fundamental choices they face is whether to opt for virtual servers or physical servers. Each option has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making the decision a critical one. In this blog, we’ll compare virtual servers and physical servers to help you make an informed choice for your organization.
What is a virtual server?
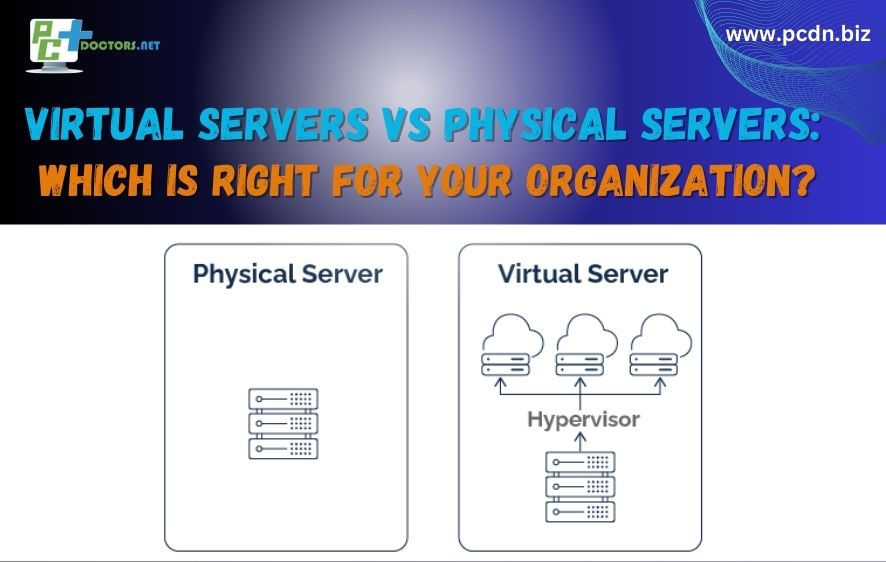
A virtual server, often referred to as a virtual machine (VM), is a software-based emulation of a physical computer or server. It allows multiple virtual servers to run on a single physical server or host system. These virtual servers are isolated from each other and can run different operating systems and applications.
How does a virtual server work?
A virtual server, also known as a virtual machine (VM), operates by leveraging virtualization technology to create a software-based representation of a physical server within a host system. This virtualization layer, known as a hypervisor, allows multiple virtual servers to run simultaneously on the same physical hardware. Each virtual server operates independently with its own operating system and applications, making it appear as if it is running on a dedicated physical server. This technology enables efficient resource utilization, scalability, and isolation, making it a flexible and cost-effective solution for an organization.
Advantages and disadvantages of virtual servers:
Virtual servers offer numerous advantages, but they also come with some disadvantages. Here’s a summary of both:
Advantages of Virtual Servers:
1- Cost Savings: Reduced hardware and maintenance costs, as well as lower energy bills, lead to significant savings.
2-Scalability: Easily add or remove virtual servers to meet changing workload demands, offering flexibility and agility.
3-Resource Allocation: Allocate resources dynamically based on workload, ensuring optimal performance for each virtual server.
Disadvantages of Virtual Servers:
1-Complexity: Managing virtualization environments can be complex, especially in larger deployments.
2-Lack of Control: In a public cloud environment, you have limited control over the underlying infrastructure, which can be a concern for some organizations.
3- Security Concerns: Virtual servers share a physical host, so a vulnerability in the hypervisor can potentially affect all VMs on that host.
What is a physical server?
A physical server is also commonly referred to as a “bare metal server.” A physical server, often referred to simply as a server, is a physical computer system that is dedicated to running various software applications and services.
How does a physical server work?
A physical server is a standalone computer system that operates independently, running an operating system and hosting various applications or services. It works by utilizing its dedicated hardware resources, including the CPU, memory (RAM), storage drives, and network interfaces, to process and manage data and perform tasks as required. Physical servers are often deployed in data centers or server rooms, where they provide dedicated and reliable computing power for specific applications or workloads.
Advantages and disadvantages of physical servers
Physical servers have several advantages and disadvantages, which are important to consider when choosing between physical and virtual server infrastructure. Here are some of the key advantages and disadvantages of physical servers:
Advantages of physical Servers:
1- High Performance: For resource-intensive applications, physical servers can deliver high and consistent performance, without the overhead associated with virtualization.
2- Security: Physical servers can be more secure since they have a lower attack surface, making them suitable for applications with stringent security requirements.
3-Licensing Costs: In some cases, you may save on virtualization software licensing costs, as physical servers do not require a hypervisor or virtualization layer.
Disadvantages of physical Servers:
1-Limited Scalability: Scaling a physical server typically involves adding or upgrading hardware, which can be costly and time-consuming compared to the ease of scaling virtual servers.
2-Maintenance Challenges: Hardware maintenance can be complex, requiring regular updates, monitoring, and potential downtime for repairs or upgrades.
3-Higher Hardware Costs: Setting up and maintaining physical servers may require a larger initial investment in hardware, including servers, storage, and networking equipment.
Virtual Servers vs Physical Servers: Which is Right for Your Organization?
Who should consider a virtual server?
Virtual servers are well-suited for organizations and individuals who require flexible, cost-effective, and scalable computing resources. They are ideal for those looking to optimize resource utilization, reduce hardware and maintenance costs, and easily scale their infrastructure to accommodate changing workloads. Virtual servers are especially beneficial for development and testing environments, web hosting, small to medium-sized businesses with budget constraints, and organizations that need rapid provisioning, redundancy, and disaster recovery capabilities without the limitations of physical hardware.
Who should consider a physical server?
Organizations that should consider using physical servers are those with specific requirements for dedicated and high-performance computing resources, as well as stringent security or compliance needs. These organizations often include enterprises running resource-intensive applications like large-scale databases, high-performance computing, and mission-critical services. Additionally, businesses with legacy systems or applications that cannot be easily migrated to virtualized environments may find physical servers to be a practical solution. Furthermore, industries such as healthcare, finance, and government, where data security and regulatory compliance are paramount, may opt for physical servers to maintain tighter control over their infrastructure.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the choice between virtual servers and physical servers hinges on the unique needs and goals of your organization. While virtualization offers flexibility and resource optimization, physical servers provide dedicated power and security. To make the best decision for your business, it’s essential to evaluate your specific workloads, performance requirements, and budget constraints. Regardless of your choice, having a trusted partner to guide you through this critical decision is paramount. That’s where PC Doctors.NET comes in. With a global presence and a team of experts, PC Doctors.NET offers a comprehensive range of IT solutions to empower your organization. Partner with PC Doctors.NET and unlock the full potential of your IT infrastructure. Your success is our mission. Give us a call at +1 (346) 355-6002 (USA) / 1800-889-0674 (IND) / +44 (208) 089-3489 (UK).